How to create a Ubuntu bootable USB using MacOS

What you need beforehand – Prerequisites
- At least 4 GB USB device – pen drive >= 4 GB size
- Ubuntu Desktop OS – Official Ubuntu Download Page
- Etcher app – Official Etcher Download Page
- Mac or laptop running MacOS
sudoaccess permission.
Before continuing to this tutorial, please read this important checklist as the last section of this page. It consists of common mistakes and foretold issues that can slow you down the road. It can save your time from searching the internet resources for solutions.
Jump to sections: Step 2: Download, Step 3: Flash OS
Step 1: Erase and Ready USB drive
- Insert the USB drive into the port. Make sure the drive is detected and functioning properly without any warnings.
- Next, hit CMD+space to open up Spotlight search on your macOS. Search for “disk utility” and open
Disk Utility. Alternatively, you can also open it from Applications > Utilities.
Disk utility detects and shows your USB device in the External on the left panel. Confirm your USB device by cross checking with the details like Capacity, Name and Connection.
- Select the USB device from
External. Find and Select the “Erase” option from the top toolbar.
Don't panic or hassle at this crucial step. Selecting wrong drive can cripple and delete everything from your disk drives.
A dialogue box pops up before proceeding to the format operation.
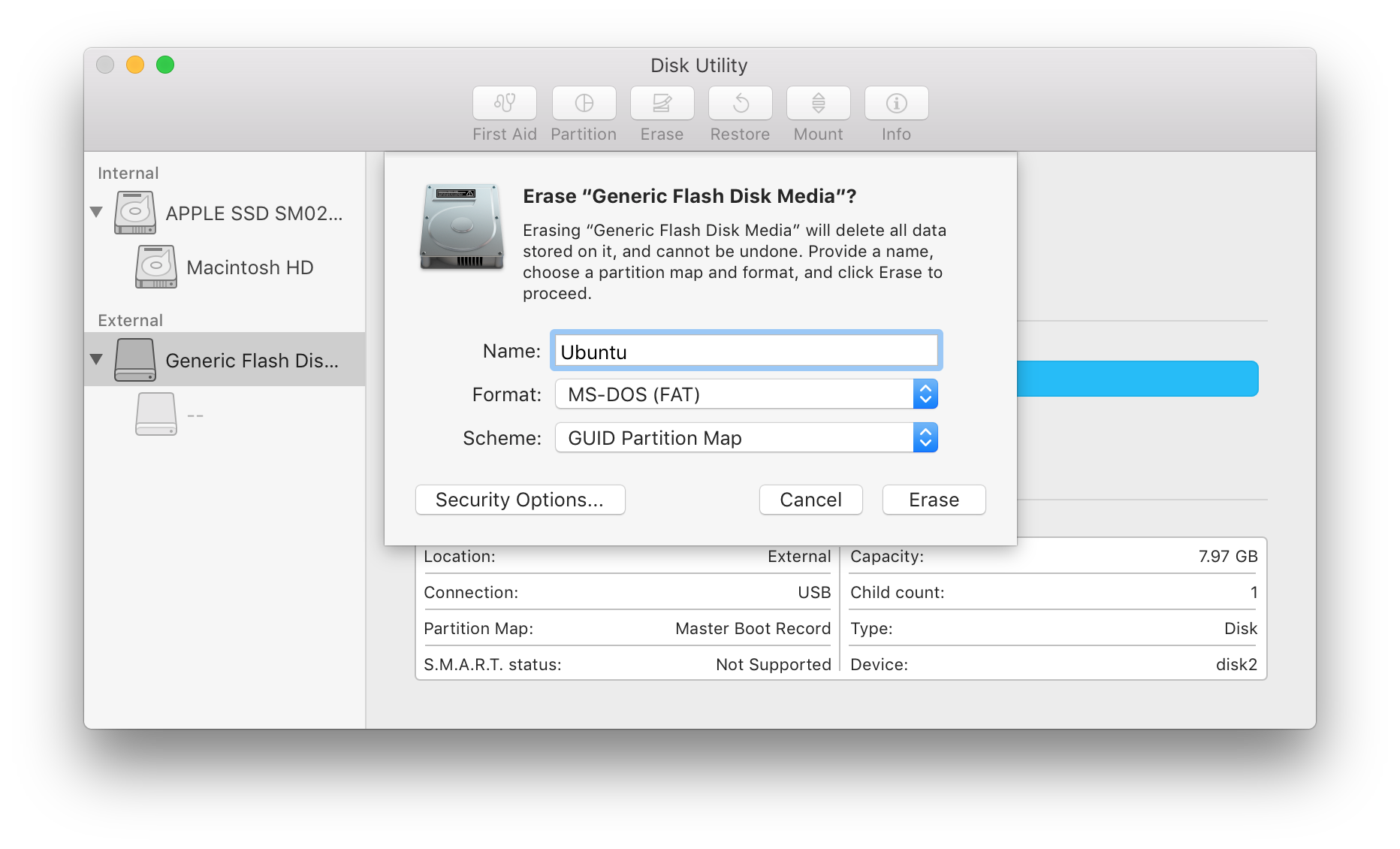
- Select “Format” and change to
MS-DOS (FAT)orMac OS Extended (Journaled) - Select “Scheme” and change to
GUID Partition Mapor if the option is disabled, then leave it as it is. - Now, check everything and hit “Erase” to start the formatting USB drive.
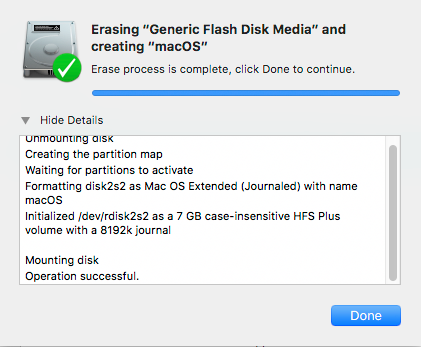
After successful format, you should see something like this. USB device is now ready.
Step 2: Download, install and run as sudo – Etcher app for macOS
Etcher by balena.io (resin.io) is a GUI standalone app running in Win, Linux, MacOS that flashes OS images onto USB drives and SD cards.
- Download the latest macOS version of Etcher app from the official page.
After downloading the macOS version of Etcher, you should have a dmg file around 80MB similar to balenaEtcher-x.y.z.dmg.
- To install Etcher, double click to open the dmg file. Drag the app icon to Applications folder to sync and mount the package. In case of permissions, work accordingly by entering your user password.

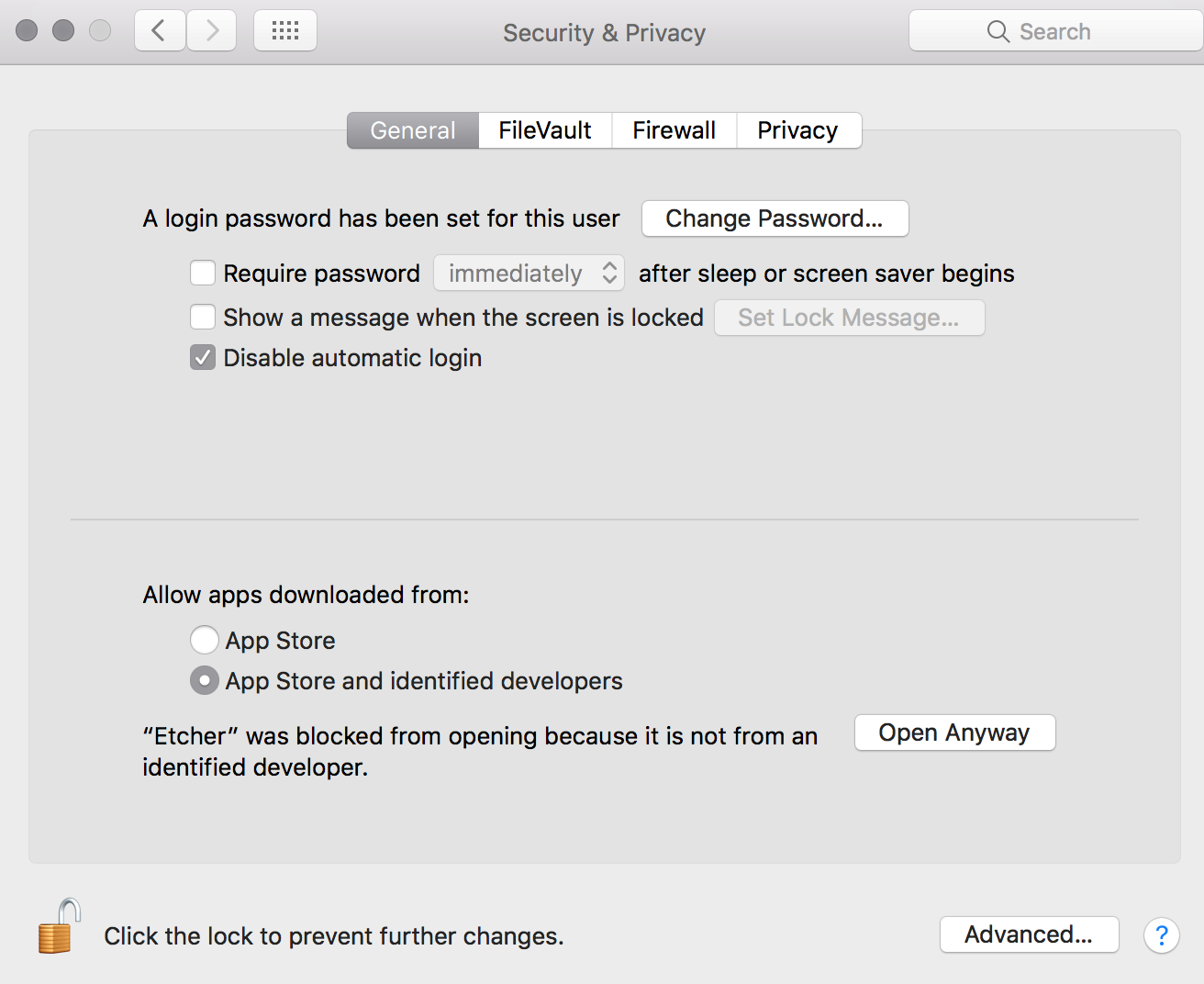
- By default, newer macOS versions block the apps from unidentified developers. To solve this same issue with Etcher, click ‘Open Anyway’ in the ‘Security & Privacy’ panel of
System Preferences. Click the lock to save your changes.Enabling "App Store and identified developers" in the "Security & Privacy" panel of "System Preferences" is a bad habit of making your system vulnerable to unknowingly dangerous apps in future.
- Next, to run Etcher with
sudopermission, open up mac terminal from Spotlight search (CMD+space) and get ready for some bash commands. - In your terminal,
~ cdApplications/balenaEtcher.app/Contents/MacOS
This is where the unix file ofbalenaEtcherresides that needs to be run assudo.
~ sudo balenaEtcher
(prompts for sudo password)
Now, you should be running Etcher withsudoaccess.
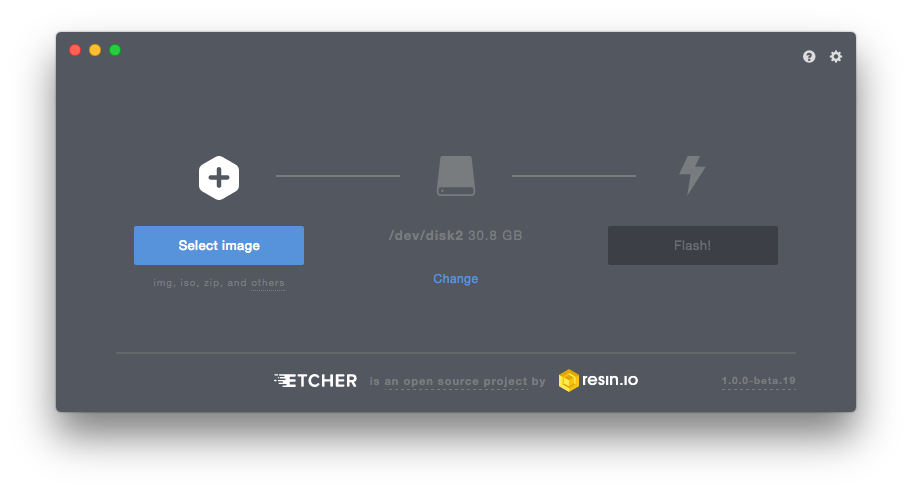
Step 3: Convert and Flash OS image
By now, assumed you have downloaded the ISO image of Ubuntu Desktop from the official page. We need to convert the ISO image into the DMG format with the help of hdituil available from your macOS.
- Open up mac terminal and convert
.isoto.dmgwithhdituilusing the command:
~hdiutil convert /path/to/ubuntu.iso -format UDRW -o /path/to/target.img
MacOS puts the .dmg ending on the output file automatically. - Now using the Etcher app,
Select Image > Navigate and choose the recently converted.dmgfile of Ubuntu. Better to look first inDownloadsfolder. - Select Drive and make sure it is set with the target USB device prepared since the Step 1. Etcher should detect the inserted USB device. If not, find solutions in these resolved github issues of Etcher.
- Check everything one last time, and click
Flash!
Enter your computer password and initiate the flashing process.
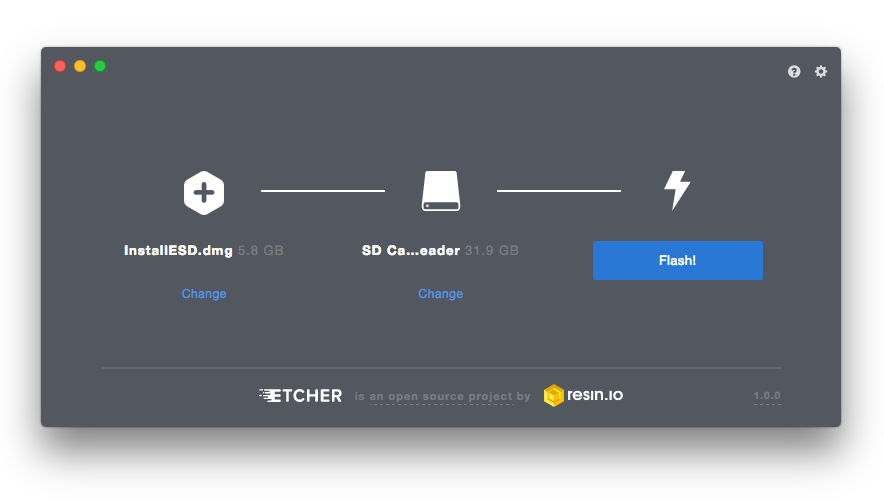
Wait for the operation to complete successfully and safely eject the USB device after you get something like this.
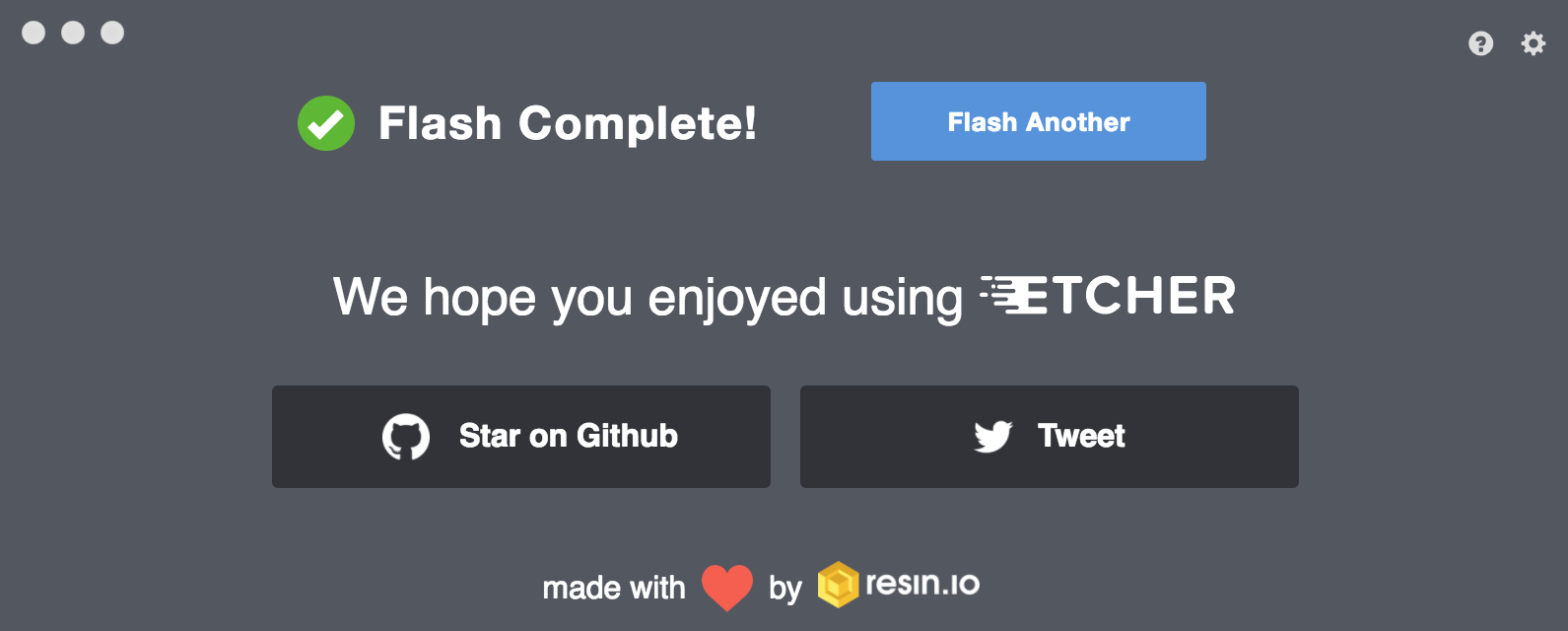
Congrats! you have successfully created the latest Ubuntu Desktop OS bootable on your USB device and ready to go.
Important checklist:
- Make sure the USB drive is not corrupted or malfunctioning. Sometimes old USB drive looks fine but the clusters are crippled within the drive that results in unknown and vague errors during the process like below.
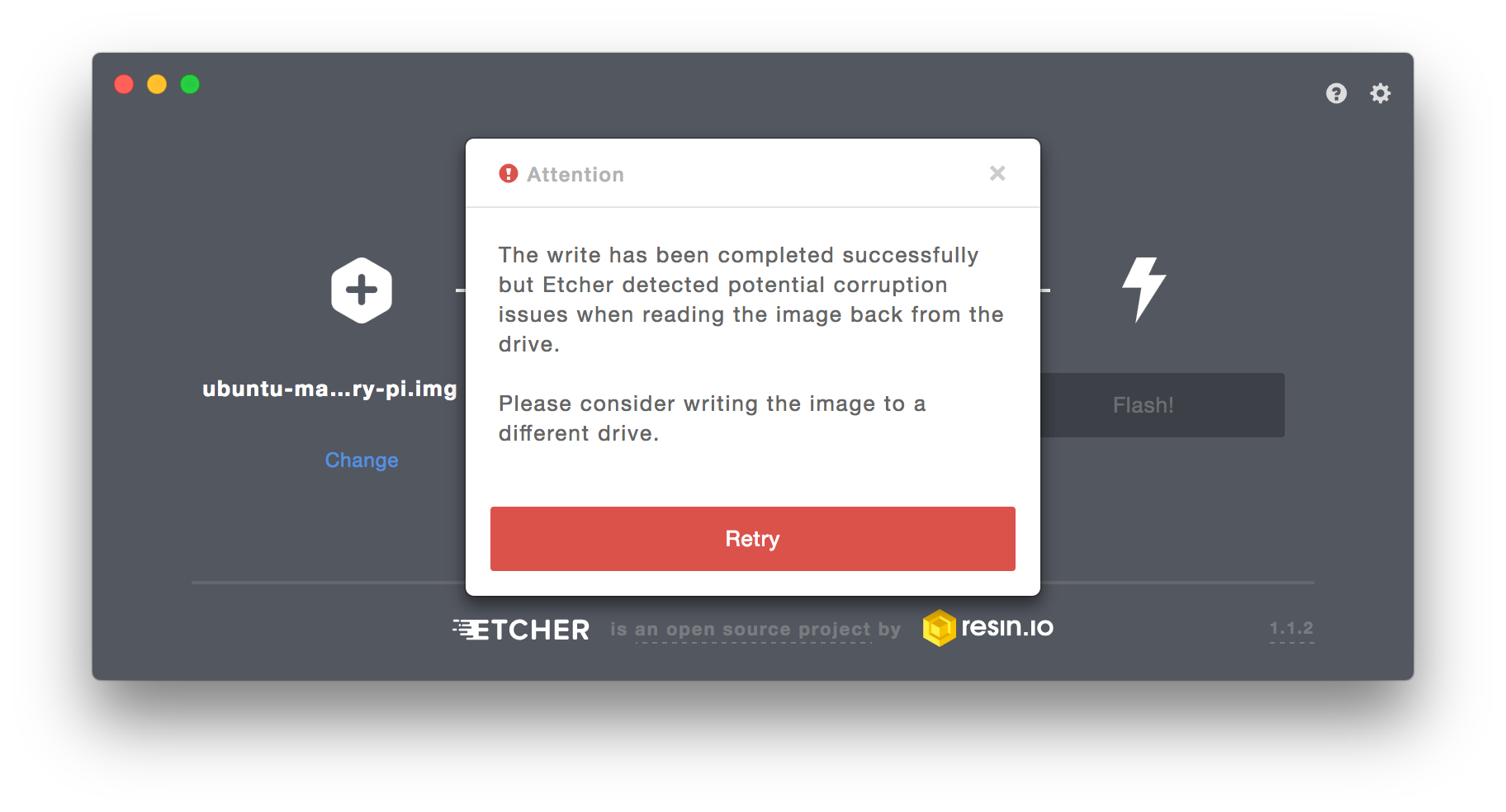
USB capacity must be at least 4GB. Having more size or more space doesn't speed up the process; it's just a myth. However, USB drives with 3.0 interface being faster than USB 2.0 interface is not a myth. Use latest.
- Ubuntu has 4 main types of OS distributions viz. Ubuntu Cloud, Ubuntu IoT, Ubuntu Server and Ubuntu Desktop.
In general, we use Ubuntu Desktop as our main OS for our goto option. - Meanwhile we also need
sudoaccess with this tutorial because of the application Etcher that will be used for flashing. Without thesudoaccess, the Etcher app would create problems like reported in this github issue.
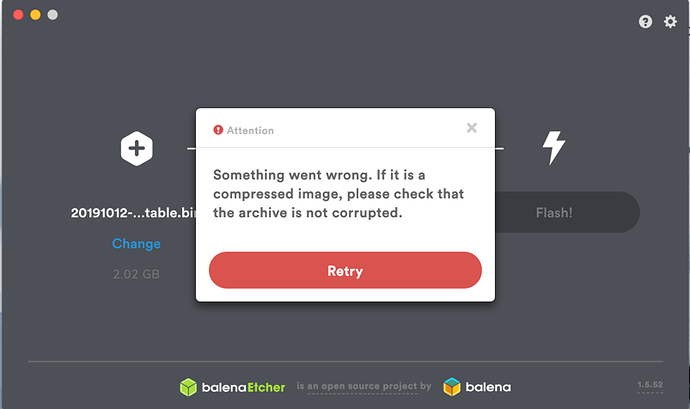
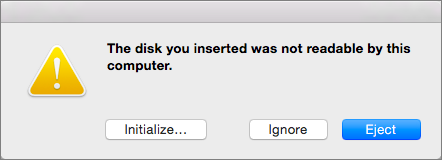
- At the end of successful flash, macOS may even warn you with error like ‘The disk you inserted was not readable by this computer’. Don’t select Initialise. Select Eject and remove the USB device. Even you did no worries as long it works as life goes on.
Thank you for reading to the end of this article.